In new energy vehicles, the battery is a critical module and a key differentiator from traditional fuel vehicles. It is widely known that copper alloy busbars are widely used in the battery connections of new energy vehicles, but few people are familiar with the specific characteristics of this material. Now, let me unveil the related knowledge of copper busbars used in new energy vehicles.
First of all, in the battery system, the electrical connections used to connect the modules do not vary with the shape of the battery cells.
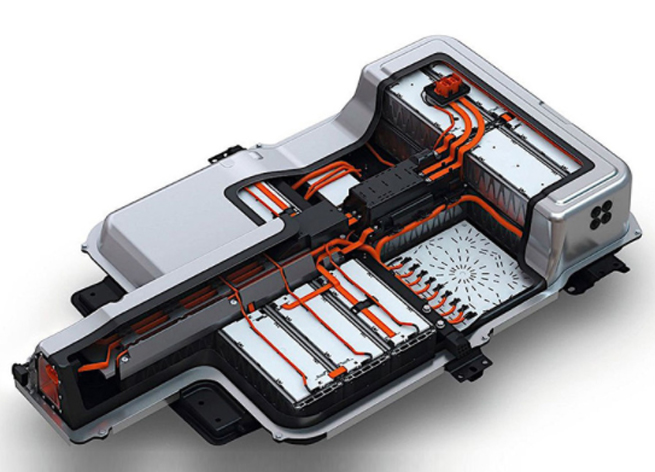
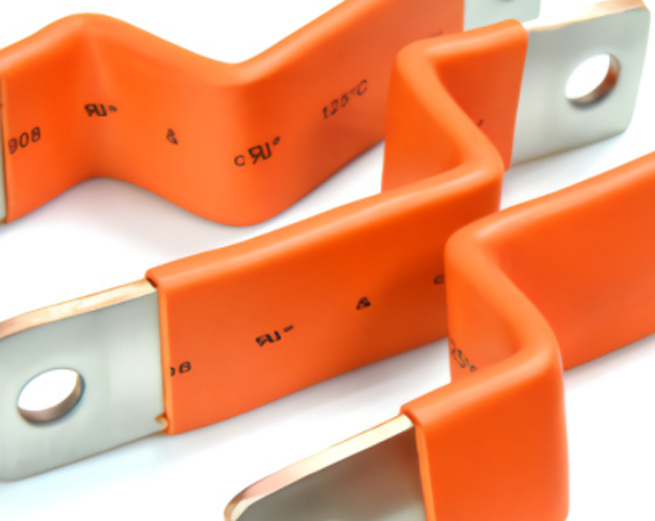


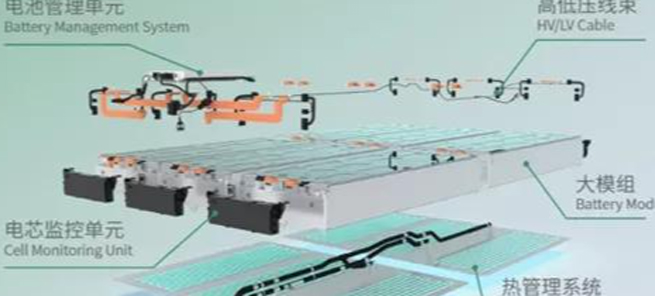

There are generally three methods for connecting battery modules.
First: Flexible Connection
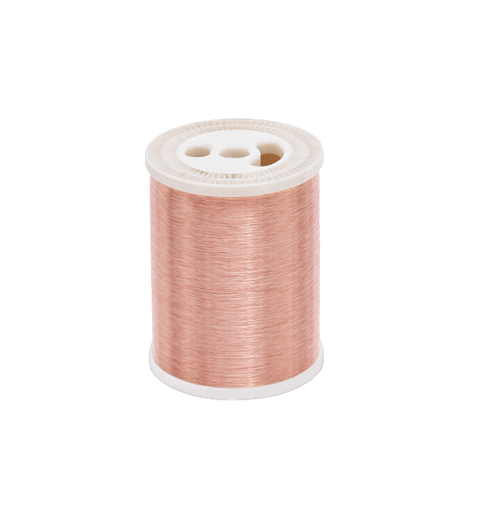
Flexible busbars are made up of multiple layers of flat copper foil conductors with anti-electrostatic insulation layers. The outer layer is made by extrusion molding with insulating layers. Generally, flexible connections use 0.1mm copper strip as raw material and cut it according to the design requirements of the drawings.
For contacts that need to be bonded with nickel plates on both ends, customers need to specify whether it is for the entire strip or only for specific areas. The cut raw materials are designed according to the requirements of the drawings, and they are formed by high-current and high-temperature pressure welding through polymer diffusion welding according to the welding requirements.
The advantages of flexible busbars are very obvious. In terms of performance, multiple batteries are usually connected in series in the battery to obtain the required operating voltage. If higher capacity current is required to obtain more power, it is possible to consider connecting two or more batteries in parallel.
The copper strip products produced by Jintian Copper fully meet the size requirements of 0.1mm. They have a smooth surface and excellent conductivity performance. They are the preferred raw materials for soft connections chosen by first-tier battery manufacturers in China.
Second: Hard Connection
Hard connections, also known as hard busbars, are made of copper and have a rectangular or chamfered (rounded corner) rectangular cross-section conductors. This type of material generally includes copper and aluminum. Aluminum-made materials are called aluminum busbars. They play the role of transmitting current and connecting electrical equipment in circuits.
As one of copper busbars suppliers, Jintian Copper offers copper busbars with excellent mechanical properties and weldability, can carry large currents, and can maintain stable performance under extreme conditions.
Third: Round Wire
This solution is widely used in the industry, especially in the early development of battery module connection technology. However, now many battery modules have abandoned this solution due to spacing issues in module layout.
In terms of craftsmanship, the processing technology of flexible busbars and hard busbars is relatively simple. However, in the industry, the entire process of process preparation, raw material storage and placement, finished product packaging and processing are relatively rough. With the vigorous development of the automotive industry, on-site management and process level of various materials processing urgently need to be improved.
Overall, the processing flow of copper busbars is roughly as follows:
Standard material selection-cutting-acid pickling-slicing-welding-pressure flattening-side cutting-punching-insulating outer layer surface-polishing-tinning-packaging
From a standard perspective, copper busbars are widely used in the electrical industry.
The Main Standards Applied Domestically Are as Follows
GB/T5023 Insulated Cable Standard
GB7251-2008 "Low-voltage complete switchgear"
GB5585.1-2005 "Copper, Aluminum, and Their Alloy Busbars for Electrical Purposes" Part 1: Copper and Copper Alloy Busbars
The Main Standards Applied Abroad Are as Follows
International Electrotechnical Commission IEC 61439-1-2009 Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies - General rules
International Electrotechnical Commission and IEC 61439-1-2011 Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies - Part 1: General rules for components
UL 67 approved "Panelboards and Distribution Boards"
UL 758 approved components belonging to "Equipment Wiring Materials - Components" categories 10531 and 11343
American Bureau of Shipping (ABS®) for marine and offshore applications, etc.

 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español italiano
italiano العربية
العربية tiếng việt
tiếng việt Türkçe
Türkçe ไทย
ไทย 中文
中文









