As we all know, USB Type-C (abbreviated as USB-C) has become more and more popular in our daily lives. Its symmetrical design allows for reversible insertion and has gained favor from many electronic product manufacturers. Therefore, many electronic devices currently on the market are using the Type-C standard.
Although Type-C has a new interface size and a unique name, many people mistakenly believe that it is a completely new USB standard. In fact, Type-C is a member of the USB family. Strictly speaking, it is part of the USB 3.1 standard and not a completely new standard. Type-C was born at the end of 2013 and was officially included in the USB 3.1 standard in 2014. It is a new type of USB cable and connector specification. Many people compare it to the Lightning connector used in Apple phones, and they do share some similarities, such as being perfectly symmetrical and compact. In addition, it can also connect adapters, making it compatible with previous generation interfaces such as USB 3.0 and USB 2.0, which is very convenient. It is important to note that although the USB 3.1 standard still includes Type-A (commonly seen on computers) and Type-B (commonly seen on Android phones) interfaces, Type-C is just one type of USB 3.1 high-speed data transmission and not the only one.
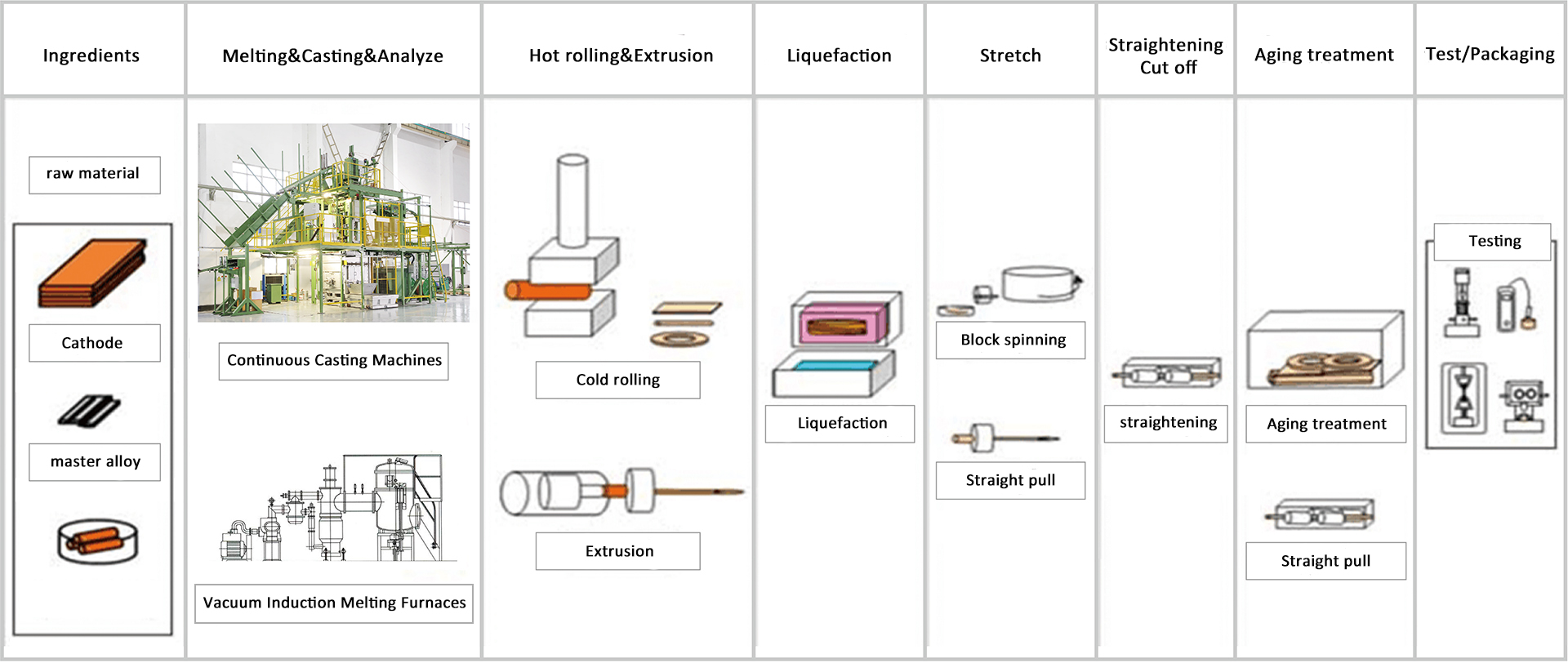
Now many people may be curious about how the Type-C connector is manufactured. Let us reveal it to you.
The main production process of Type-C:
Stamping
This includes stamping the shell and the USB terminal. The terminal is a core component of USB and is the part that contacts the Type-C male or female connector. The quality of the terminal material directly affects the performance parameters of the final product. The Type-C connector terminal is usually stamped from a thin copper strip.
Generally, one end of a large coil of copper strip is fed into the front end of a high-speed stamping machine, while the other end passes through the hydraulic worktable of the stamping machine and is wound into a coil by the coiling wheel. The coiling wheel pulls out the copper strip and coils it to stamp out the finished product.
Plating
After the terminal is stamped, it undergoes the plating process. During the plating stage, various metal coatings will be applied to the contact surface of the terminal or the shell according to the type and purpose of the product. This has higher requirements for the copper strip. The copper strip plays a key role in the performance of the connector product and meets the requirements of key indicators such as mechanical performance and electrical performance. These include elongation performance, forming performance, welding performance, and plating performance. In addition, the ability to conduct large currents and high-speed electrical signals without self-heating is also important. High elasticity and resistance to stress relaxation are key to ensuring that the connector can work in high-temperature environments without performance degradation.
The high-performance copper alloy tapes produced by Jintian Copper Group cover various categories such as red, yellow, and purple. With the support of internationally advanced production equipment and high requirements for on-site management standards, the H65, C5190, C5191, C7025, and other products produced can ensure consistent and stable performance in high-strength and complex environments, and have been widely recognized by industry customers.
Injection Molding
Injection molding of the core of the USB connector is the process of injecting high-temperature melted PBT or LCP plastic into the metal mold, and then rapidly cooling and shaping it.
Assembly
The last process is assembly. The semi-finished products produced in the previous steps are quickly assembled into finished products using high-speed assembly terminal machines, and can be officially marketed.
Our company was established in 1986 and has been focusing on the copper processing industry for 36 years. We are a leading global manufacturer of copper alloys and advanced materials. Our main products include copper pipes, rods, wires, tapes, electromagnetic wires, valves, magnetic materials, and high-end alloys such as brass, bronze, purple copper, and white copper. We are committed to providing world-class products and services for the development of industries such as new energy vehicles, 5G communications, clean energy, and consumer electronics.

 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español italiano
italiano العربية
العربية tiếng việt
tiếng việt Türkçe
Türkçe ไทย
ไทย 中文
中文